Understanding the Fundamentals of Trade School
What is a Trade School?
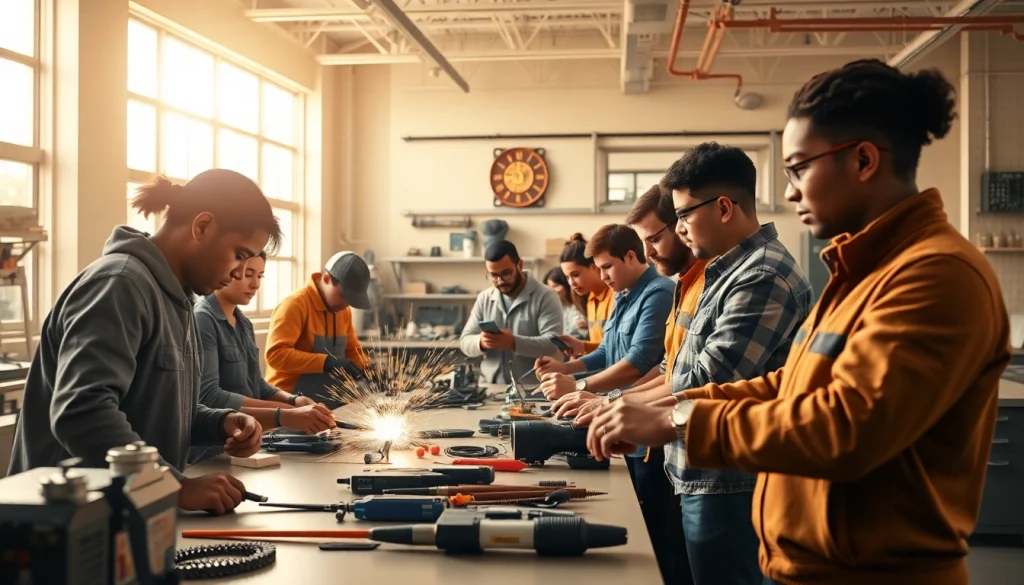
A trade school, often referred to as a vocational school, is an educational institution that prepares students for a specific trade or career, providing both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Unlike traditional four-year colleges, trade schools focus on specialized training in fields such as plumbing, electrical work, automotive repair, culinary arts, and healthcare. With programs designed to be intensive and career-oriented, trade schools equip graduates with the hands-on experience necessary to enter the workforce quickly and effectively. For those considering this path, exploring trade school options is a pivotal first step.
Benefits of Attending a Trade School
Attending a trade school comes with numerous benefits. Primarily, trade schools provide a faster route to employment compared to traditional college degrees, with many programs lasting only a few months to two years. This accelerated schedule allows students to enter the workforce sooner, earning a steady income without incurring the high debt often associated with lengthy college programs. Additionally, trade schools typically offer lower tuition costs, making them an affordable option for many aspiring professionals.
Another significant advantage is the hands-on learning environment that trade schools provide. Students gain direct experience with industry-specific tools and techniques, enhancing their job readiness upon graduation. Furthermore, many trade schools have established partnerships with local businesses, leading to increased job placement rates and networking opportunities.
Common Programs Offered in Trade Schools
Trade schools offer a diverse array of programs catering to various interests and career goals. Common fields of study include:
- Healthcare: Programs such as nursing, dental assisting, and medical billing equip students for essential roles in the growing healthcare sector.
- Construction: Courses in plumbing, electrical work, and HVAC prepare students for trades that are always in demand.
- Information Technology: Programs focusing on network administration, cybersecurity, and web development respond to the digital age’s demands.
- Culinary Arts: Culinary schools train talented chefs and restaurant managers, combining theory with hands-on kitchen experience.
- Automotive Technology: These programs teach students how to maintain and repair various vehicle types, meeting industry needs.
Navigating Admission Processes
Application Requirements and Steps
Applying to a trade school typically involves several steps to ensure that prospective students meet the prerequisites for their desired program. The first step is to research various trade schools, considering factors such as location, available programs, and accreditation status. Once a candidate has chosen a school, they should gather all necessary documentation, which often includes high school transcripts, identification, and potentially test scores.
Most trade schools require applicants to fill out an online application form, which may include an essay or personal statement explaining the candidate’s interests and career objectives. Following submission, some programs may call for an interview to assess the applicant’s commitment and fit for the program.
Financial Aid Options for Trade School
While trade school programs tend to be more affordable than traditional college routes, many students still seek financial aid to cover tuition and other expenses. Financial aid options for trade school students include federal and state grants, scholarships, and student loans. The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) can be completed to determine eligibility for federal aid, including Pell Grants and Direct Loans.
Additionally, many trade schools offer their own scholarships or work-study programs, providing further financial support. It’s advisable for students to explore all possible financial aid packages, as they can significantly reduce the overall cost of education.
Preparing for Interviews and Onboarding
Upon acceptance into a trade school program, the next step often involves preparing for onboarding and any associated interviews for internships or job placements. Candidates should take the time to perfect their resumes and practice common interview questions specific to their industry. Networking with instructors and fellow students is essential at this stage, as these connections can provide valuable insights and amplify job opportunities. Additionally, many trade schools offer workshops and resources to assist students in preparing for successful interviews.
Curriculum and Learning Environments
Hands-On Training and Practical Experience
One of the most advantageous aspects of trade school education is the focus on hands-on training. Many programs incorporate laboratories, workshops, and simulated environments to provide students with real-world experiences. This practical experience is instrumental in helping students master the necessary skills for their chosen trade. For instance, a culinary program may allow students to work in a fully operational kitchen, while an automotive program might involve real car repair in a shop setting.
Instructors are typically industry professionals who can offer firsthand insights and mentorship, further enhancing the quality of practical education. These experiences not only prepare students for specific tasks but also develop soft skills like teamwork and communication, which are vital in any work environment.
Online vs. In-Person Trade School Learning
As technology continues to evolve, trade schools are also adapting by offering online programs. While many trades require hands-on experience that cannot be replicated online, some theoretical components can effectively be taught through digital platforms. Online learning can provide flexibility for students who may need to balance work or personal commitments while studying.
However, students must recognize the importance of physical, hands-on training in many trade programs. A hybrid model may be the best approach for those seeking to combine the benefits of both methods. This allows students to study theory online while completing practical training in person.
Industry-Specific Equipment in Trade Schools
Trade schools pride themselves on equipping students with the latest industry-specific tools and technology. This focus on modern equipment ensures that graduates are not only skilled but also familiar with contemporary practices and tools used in their chosen fields. For example, electrical programs may include advanced training on the newest wiring systems, while automotive programs might feature diagnostics tools used in modern vehicles.
Additionally, access to updated resources prepares students to tackle challenges they’ll face in their careers effectively. This investment in quality equipment exemplifies a trade school’s commitment to delivering relevant and timely education.
Career Opportunities Post Trade School
Job Placement Rates and Success Stories
One of the significant incentives for attending trade school is the promising job placement rates. Many trade schools report high percentages of their graduates finding employment soon after completing their programs. Schools often maintain partnerships with local businesses and industries, facilitating job placement assistance for graduates. Success stories from alumni often inspire new students, showcasing notable career paths taken after graduation, whether that’s starting their own business or excelling in established companies.
Networking Opportunities and Alumni Resources
Trade schools frequently provide networking events where students can meet industry professionals and alumni who can offer mentorship and career guidance. Such opportunities allow current students to learn from those who have successfully navigated their careers post-graduation. Many institutions also have active alumni networks that can provide job leads and professional support long after students leave school.
Continuing Education and Certifications
The pursuit of knowledge doesn’t stop at graduation. Many trade school graduates pursue continuing education to enhance their skills and stay updated with industry changes. Certifications can also bolster employability, with nationally recognized credentials often leading to higher earning potentials and job advancement opportunities. Trade schools may even offer advanced courses, ensuring that their graduates can keep their skills relevant and competitive in the job market.
FAQs About Trade School
What types of careers can I pursue with trade school?
Trade school graduates can enter fields like plumbing, electrical work, healthcare, and more, offering various well-paying jobs.
How long does a trade school program typically take?
Programs may last anywhere from a few months to two years, depending on the trade and the depth of training offered.
Is financial aid available for trade school?
Yes, many schools offer financial aid, scholarships, and grants to help students cover tuition and fees.
Are trade school programs accredited?
Most reputable trade schools are accredited, which ensures quality education and may affect job placement opportunities.
Do trade schools offer job placement assistance?
Many trade schools provide job placement services, including resume workshops and interview coaching, to help graduates find work.